What is biomass energy?
Biomass energy, or energy made from plant and animal products, is a source of renewable energy. It reduces our reliance on fossil fuels (mainly oil, gas, and coal), preventing the release of carbon into the atmosphere from those nonrenewable resources. Biomass energy has the potential to be carbon neutral. This can happen if the way it is created removes the same amount of carbon from the atmosphere that it releases (e.g., if growing, transporting, processing and burning ethanol created from canola emits the same amount of carbon the canola needs to grow). Biomass energy can also be carbon neutral if it prevents greenhouse gasses from being emitted from other sources (e.g., powering generators with recycled vegetable oil from restaurants, thereby preventing those generators from being powered by coal). Although it can be carbon neutral, biomass energy is not always nutrient neutral, in that to grow and transport biomass, nutrients are required that may release greenhouse gasses (gasses that cause global warming) or pollutants. These include, but are not limited to, nitrogen compounds from fertilizer for agriculturally produced biofuels, and carbon dioxide from transporting, processing, and growing biofuels.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has expressed the importance of halving the use fossil fuels by 2030. Some of this can be done by generating more energy from woody biomass. Global biofuel production has grown in recent decades. This effort is led by the United States, but Brazil and Indonesia also produce large amounts of fuel annually.
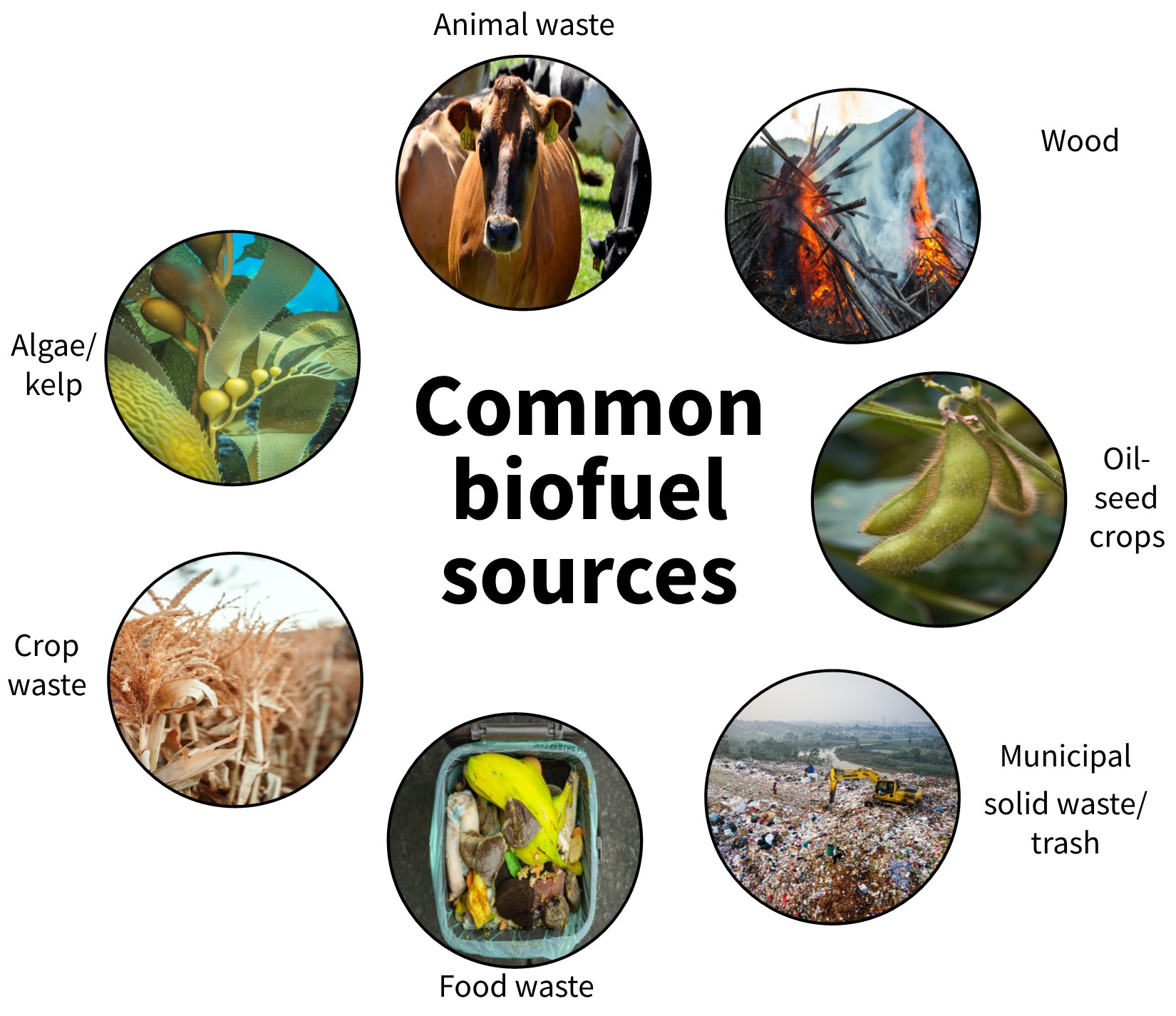
Some common sources of biofuels include:
- Agricultural products
- Oilseed crops such as corn and soybeans
- Kelp
- Agricultural waste
- Animal manure
- Food waste from unharvested crops
- Non-food cellulosic (made of cellulose, the main part of plant cell walls) products, such as:
- Crop waste and feed crop residues such as corn stalks
- Cover crops
- Plant residues left after industrial processes remove oils, sugars, starches, and protein (spent grain after brewing beer)
- Municipal solid waste
- Food waste from homes and grocery stores
- Trash
- Wood
- Slash, course and find woody debris produced from thinning or logging a forest
- Small-diameter trees removed from forests for wildland fire fuel reduction treatments
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), some potential benefits of increasing biomass energy capacity include:
- Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions when using fuels that come from agricultural or wood waste (compared to using fossil fuels).
- Decrease in fossil fuel imports, and as a result, decreased vulnerability to supply chain issues.
- Reduction of certain pollutant emissions.
- For example, increased burning of ethanol could reduce emissions of carbon monoxide.
Some considerations for potential negatives of increasing biomass energy capacity include:
- Conversion of forested lands to agriculture, as this conversion increases greenhouse gas emissions.
- Increase in crop prices, even when biofuels are created from crop waste.
- Increase in greenhouse gasses and pollutants related to growing biofuel crops (e.g., fertilizers release nitrous oxide, a greenhouse gas) and processing the biofuels.
- These increases in pollutants related to processing and growing biofuel crops could potentially lead to higher levels of greenhouse gas emissions than fossil fuels.
- Growing more biofuels may result in an increase in water pollution from fertilizer, pesticides, and sediment.
Scientists are still exploring the sustainability of biofuels to determine optimal ways to reduce atmospheric carbon. They are investigating how long it takes for the carbon that biofuels release to be reabsorbed by new plant growth and determining what types of fuels remove atmospheric carbon quickly enough for biofuels to be carbon neutral.